Smart Digital Therapeutics for Alcohol Use Disorder: Algorithms for Prediction and Adaptive Intervention
University of Wisconsin-Madison
Mental Healthcare Needs are High and Unmet
- In 2019, 52 million Americans had an active mental illness
- More than half did not receive any treatment
Mental Healthcare Needs are High and Unmet
- In 2019, 52 million Americans had an active mental illness
- More than half did not receive any treatment
- 20 million adults had an active substance use disorder
- 9 out of 10 did not receive any treatment
Mental Healthcare Needs are High and Unmet
- In 2019, 52 million Americans had an active mental illness
- More than half did not receive any treatment
- 20 million adults had an active substance use disorder
- 9 out of 10 did not receive any treatment
- Large treatment disparities exist by race, ethnicity, geography, and income
Mental Healthcare Needs are High and Unmet
In 2019, 52 million Americans had an active mental illness
- More than half did not receive any treatment
20 million adults had an active substance use disorder
- 9 out of 10 did not receive any treatment
Large treatment disparities exist by race, ethnicity, geography, and income
Failure to treat is not surprising given many treatment barriers:
- Access
- Availability
- Affordability
- Acceptability
Digital Therapeutics (DTx)
Digital therapeutics are smartphone “apps” that are designed to prevent, manage, or treat disease, including mental illness.
Can augment mental health services to address barriers
- Accessible everywhere
- Available 24/7
- Highly scalable (affordable?)
Digital Therapeutics (DTx)
Digital therapeutics are smartphone “apps” that are designed to prevent, manage, or treat disease, including mental illness.
Can augment mental health services to address barriers
- Accessible everywhere
- Available 24/7
- Highly scalable (affordable?)
- Effective!
Smart Digital Therapeutics
“Could you predict not only who might be at greatest risk for relapse …
… but precisely when that relapse might occur …
… and how best to intervene to prevent it?”
Lapse Prediction in Patients with AUD
- 151 patients with AUD
- Early in recovery (1-8 weeks)
- Committed to abstinence throughout study
- Followed for up to 3 months
- Collected active and passive personal sensing data streams


GOAL: Develop a temporally precise lapse monitoring (prediction) system for patients with AUD
Personal Sensing Data Streams
4X daily ecological momentary assessments (EMA)
Monthly self-report
Geolocation (GPS)
Cellular communications (voice and text messages)
- Meta data
- Text message content
Sleep sensor (Wake/sleep times; sleep efficiency; wakings; restlessness)
4x Daily Ecological Momentary Assessments

- Current
- Craving
- Affect
- Risky situations
- Stressful events
- Pleasant events
- Future
- Risky situations
- Stressful events
- Confidence
Feature Engineering
Features based on recent past experiences (12, 24, 48, 72, 168 hours)
Min, max, and median response (all items)
History (count) of past lapses (item 1) and completed EMAs (compliance)
Raw scores and change scores (from baseline/all past responses)
Machine Learning Methods
Predict hour-by-hour probability of future lapse
Lapse window widths
- 1 hour
- 1 day
- 1 week
Machine Learning Methods
- Statistical Algorithms
- ElasticNet GLM (e.g., LASSO, ridge regression)
- Random Forest
- XGBoost
- KNN
- Model Tuning and Performance Evaluation
- Area under ROC curve (AUC) as primary performance metric
- Sensitivity, Specificity, Balanced accuracy, Positive predictive value
- Using grouped (by participant) 10-fold CV
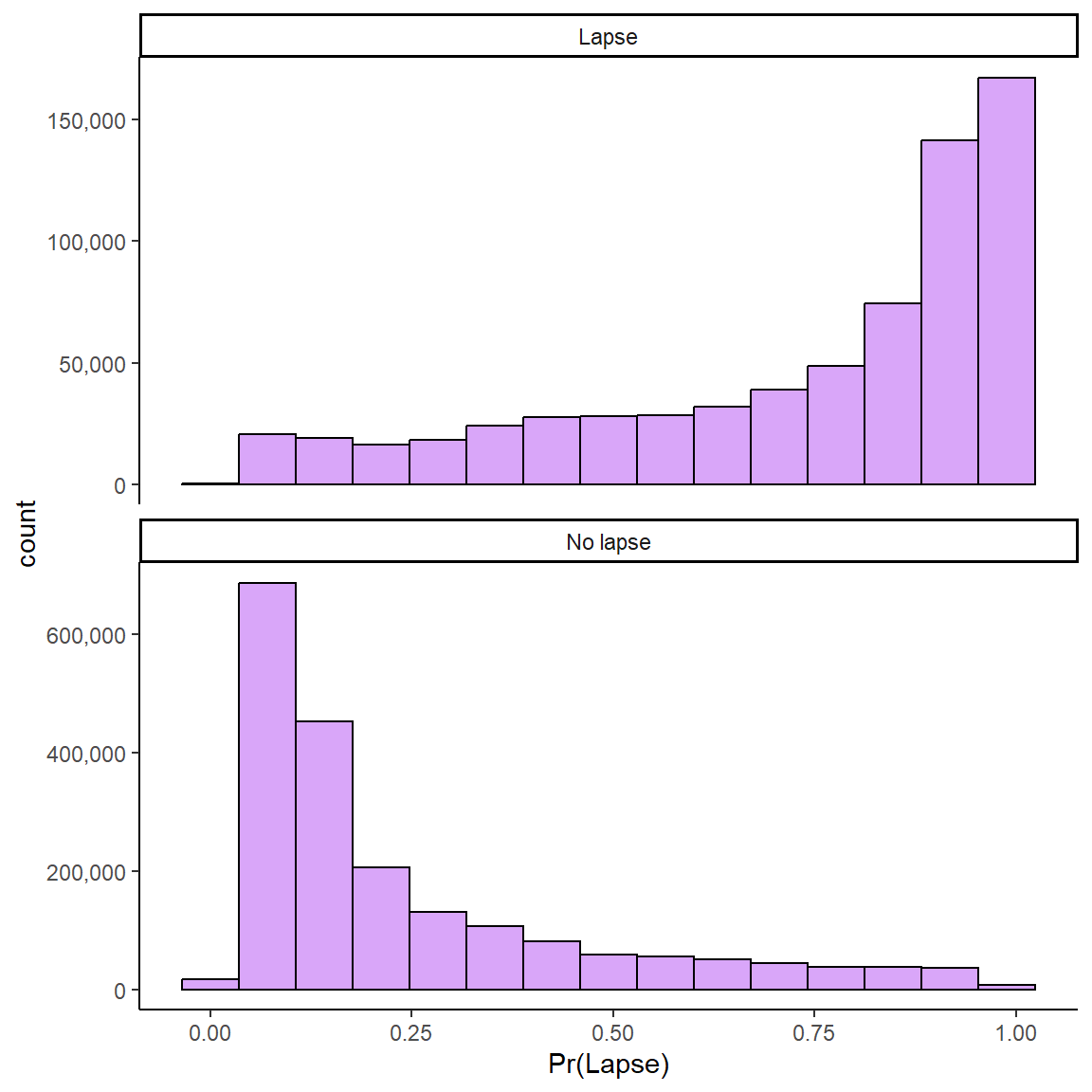
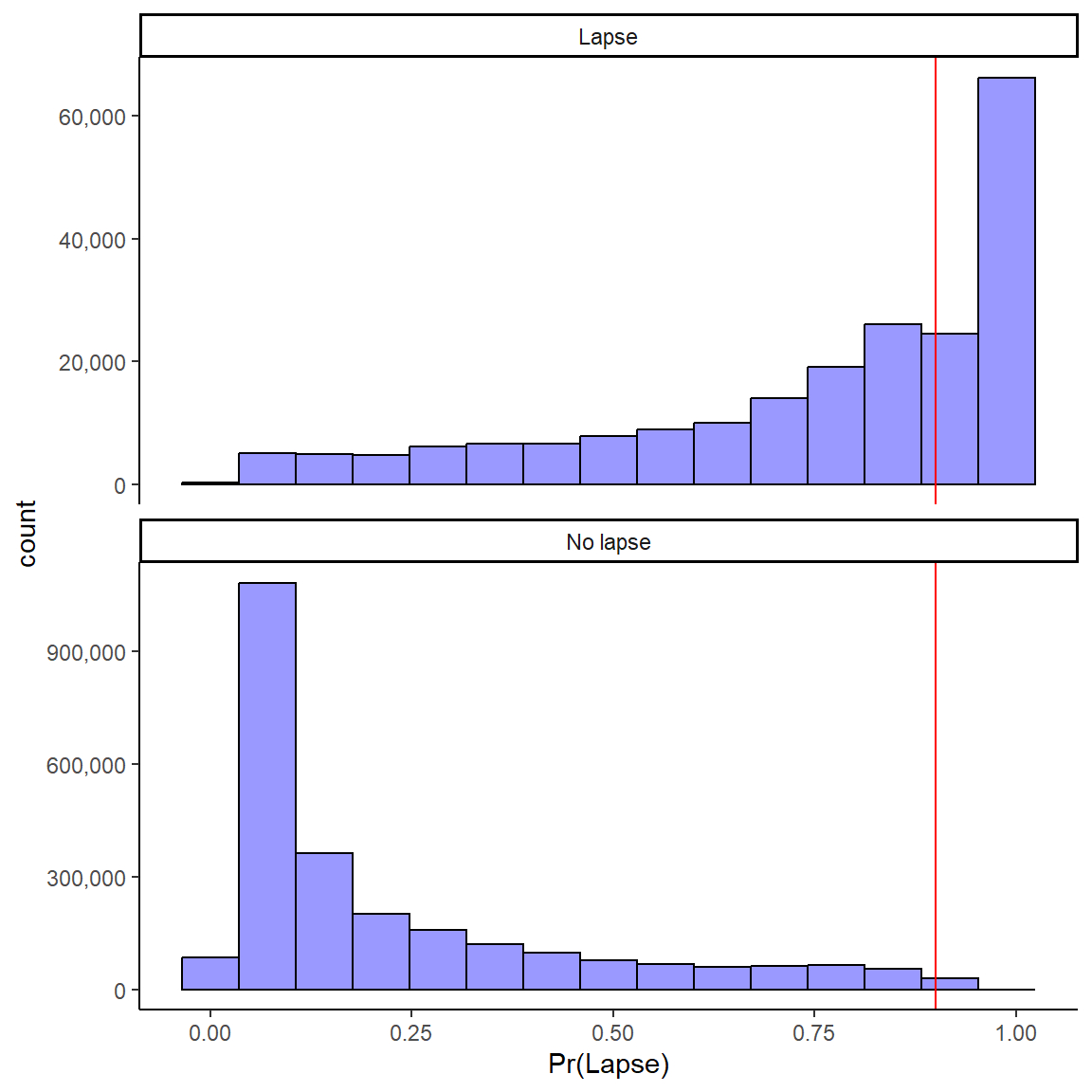
1 Week: Probabilities for No Lapse and Lapse
Model predicts probability of lapse in next week for “new” observations in test set
Can panel predictions by Ground Truth (i.e., true lapse vs. no lapse observations
Want high probabilities to be high for true lapses and low for true no lapses
1 Week: Probabilities for No Lapse and Lapse
Model predicts probability of lapse in next week for “new” observations in test set
Can panel predictions for GROUND TRUTH lapse and no lapse observations
Want high probabilities to be high for true lapses and low for true no lapses
Need decision threshold for classification (.50 default)
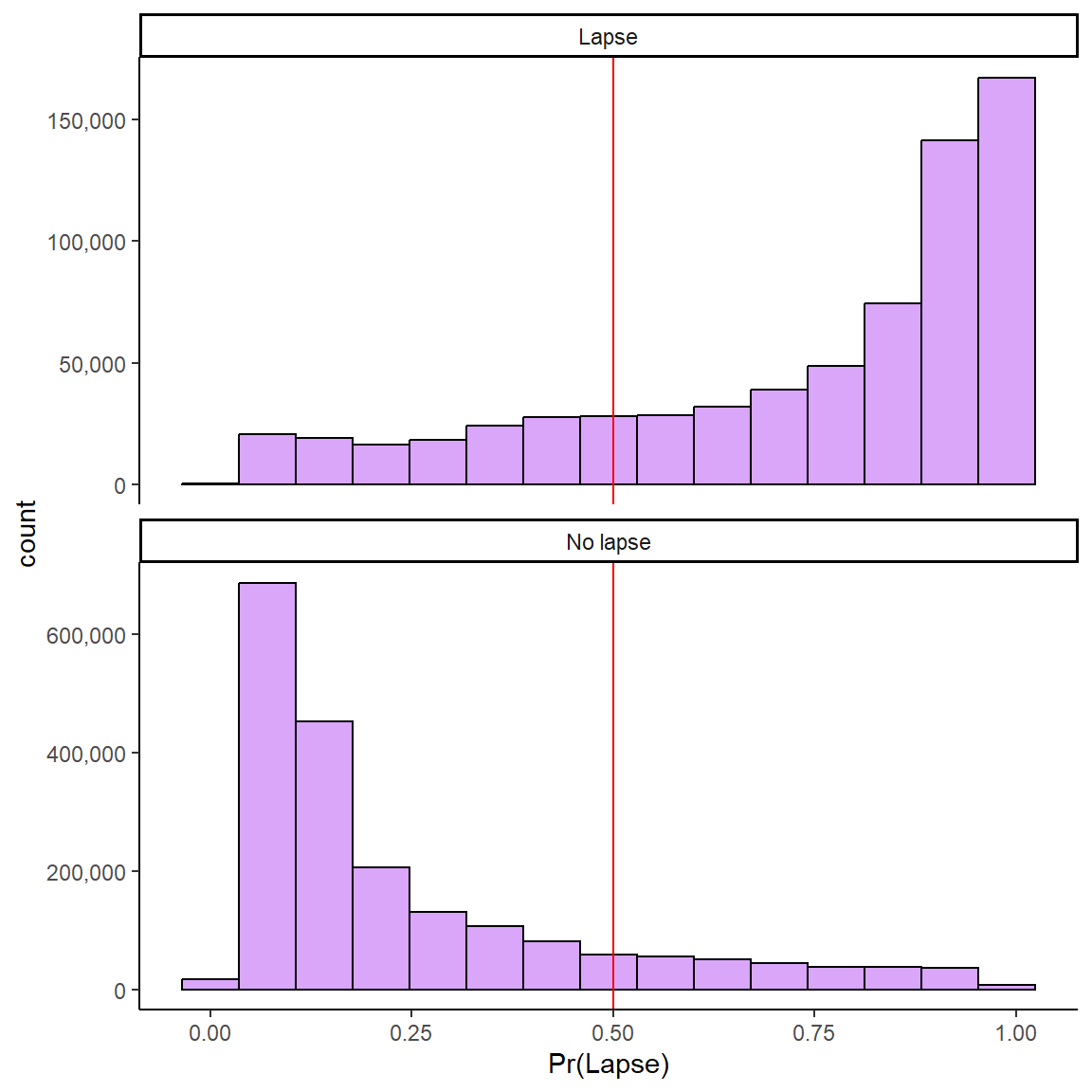
Performance Metrics by Lapse Window Width

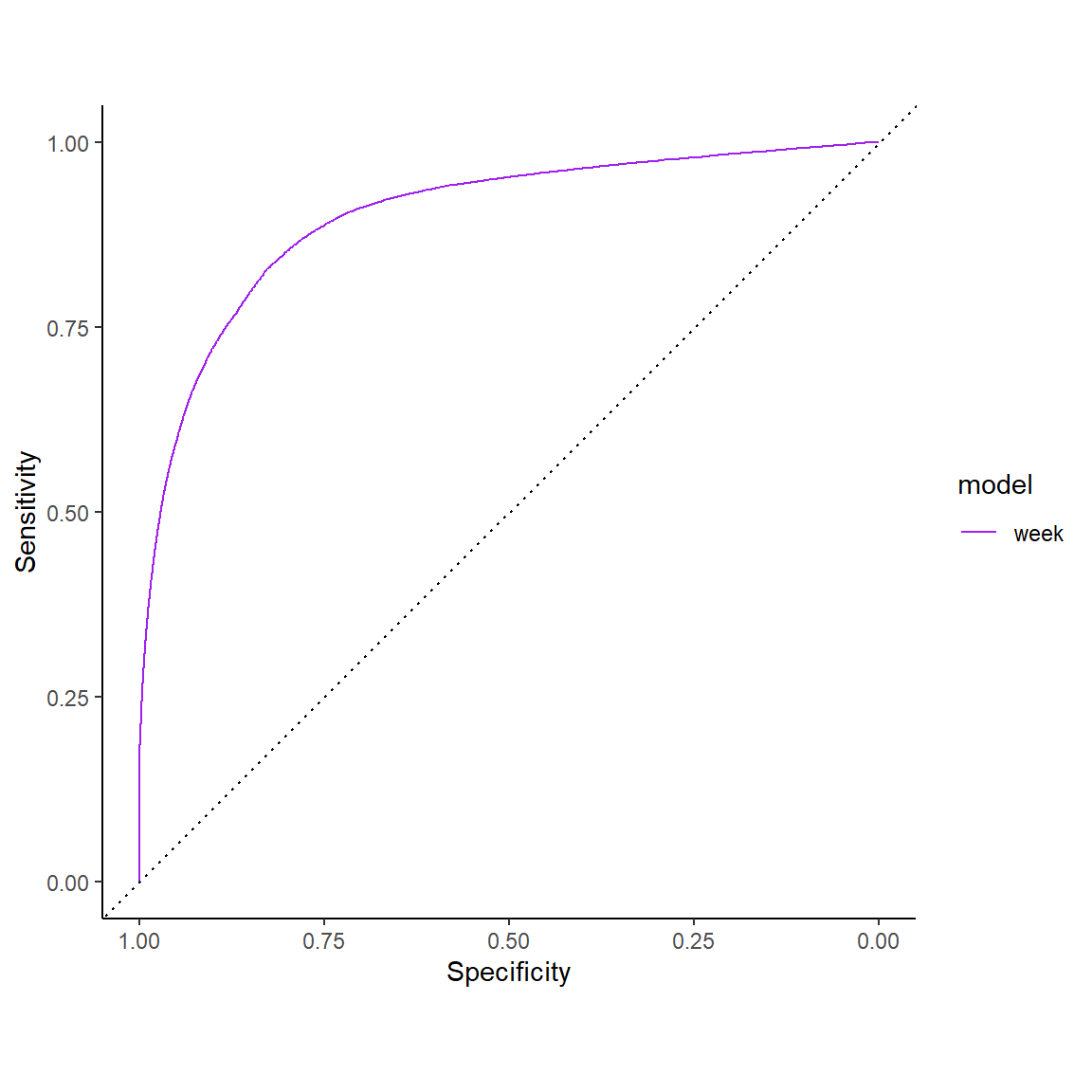
1 Week: ROC Curve
Area under the ROC curve (AUC)
Across all decision thresholds
~.5 (random) – 1.0 (perfect)
Coarse rules of thumb for AUC
.70 - .80 are considered fair
.80 - .90 are considered good
> .90 are considered excellent
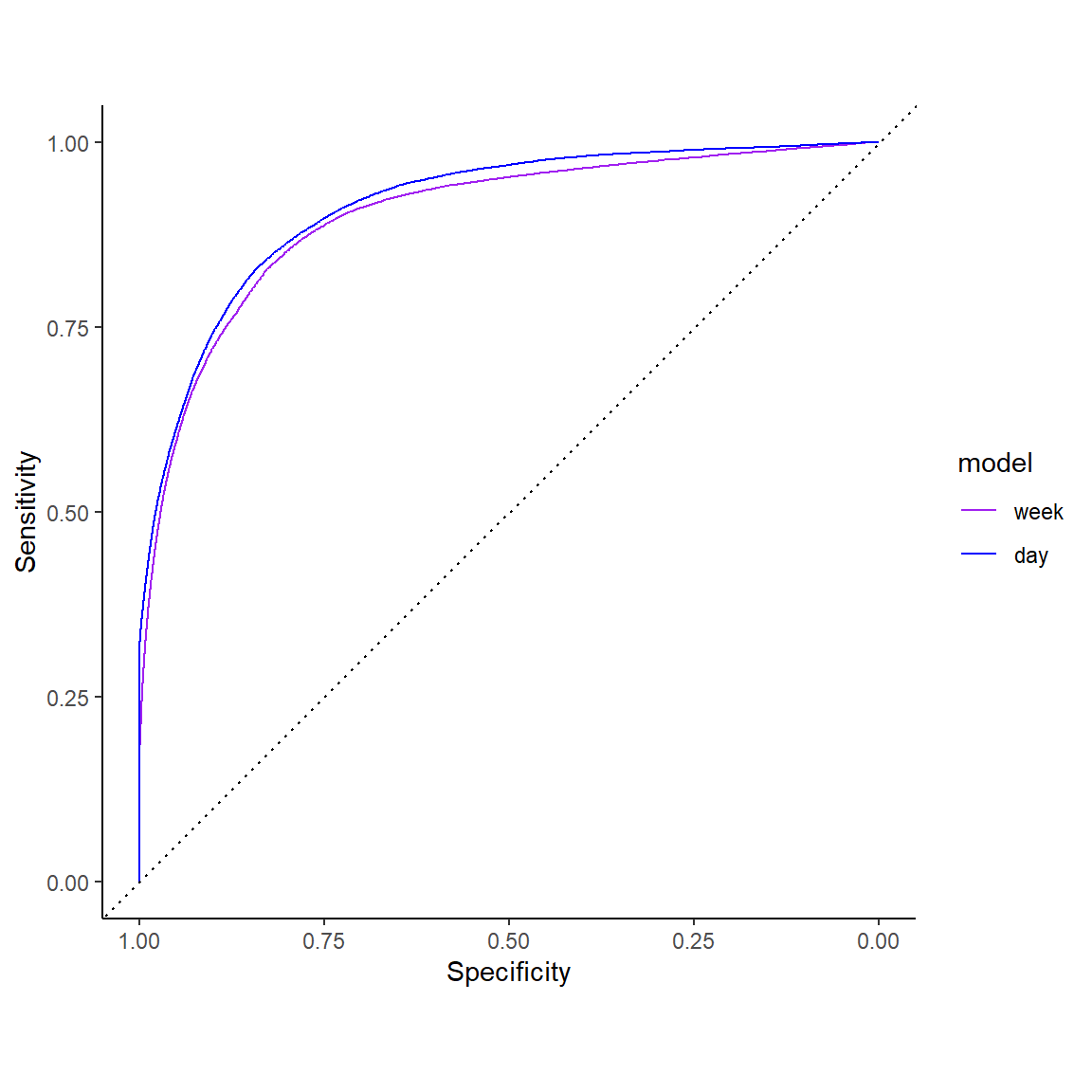
1 Day: ROC Curve
Coarse rules of thumb for AUC
.70 - .80 are considered fair
.80 - .90 are considered good
> .90 are considered excellent
1 Day: ROC Curve
Coarse rules of thumb for AUC
.70 - .80 are considered fair
.80 - .90 are considered good
> .90 are considered excellent
Performance Metrics by Lapse Window Width

1 Hour: ROC Curve
Coarse rules of thumb for AUC
.70 - .80 are considered fair
.80 - .90 are considered good
> .90 are considered excellent
1 Hour: ROC Curve
Coarse rules of thumb for AUC
.70 - .80 are considered fair
.80 - .90 are considered good
> .90 are considered excellent
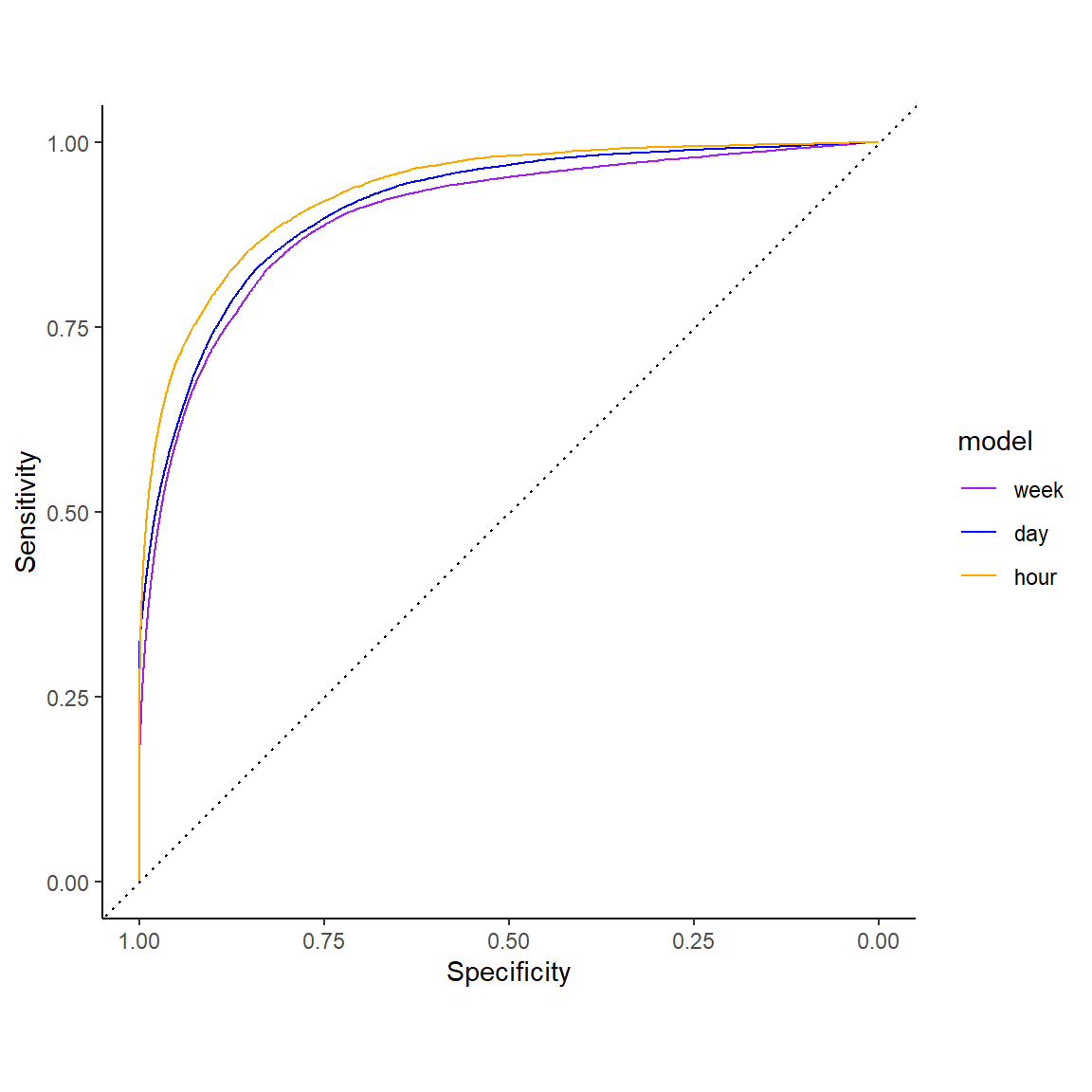
Performance Metrics by Lapse Window Width

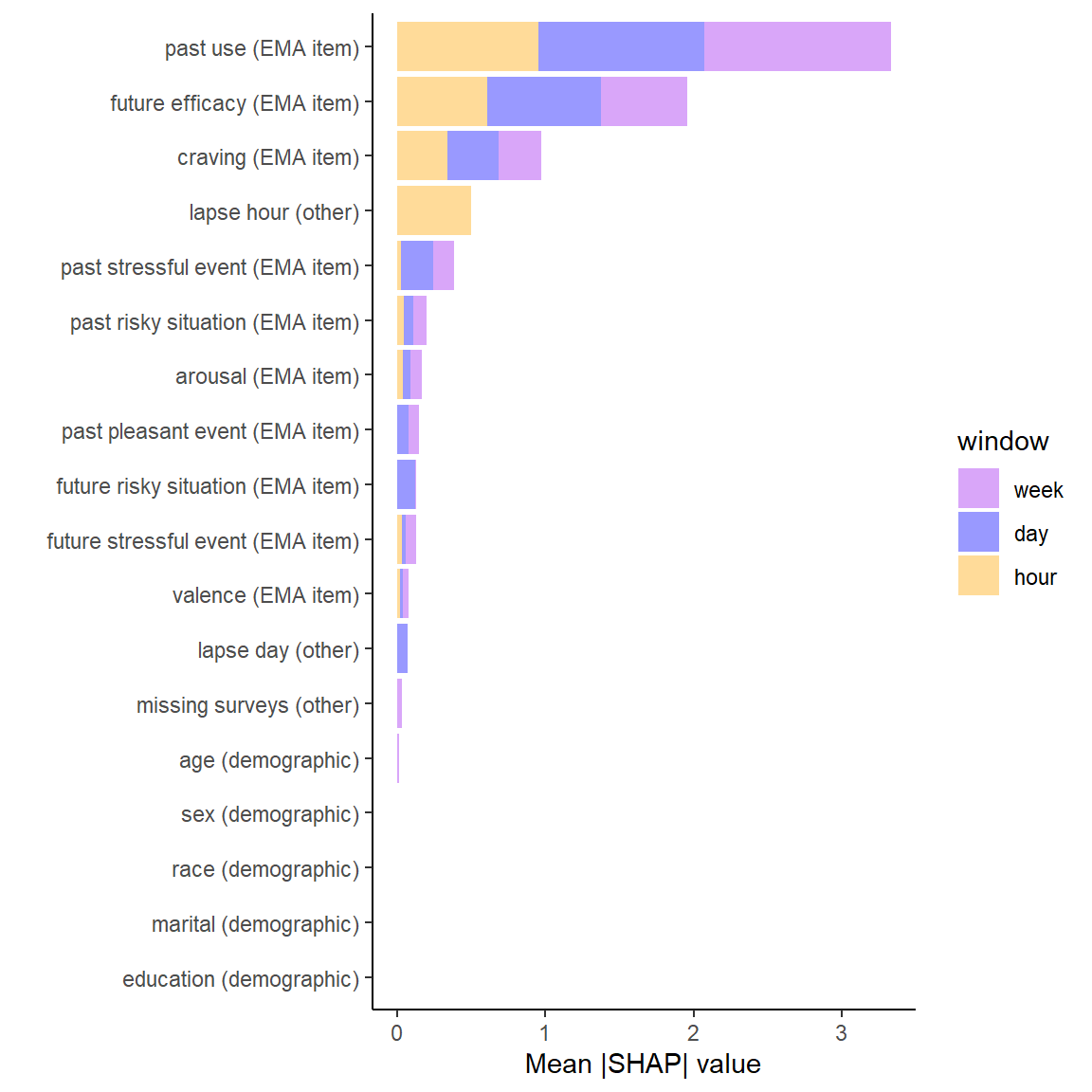
Global Variable Importance by Model
- All EMA items impact lapse probability (both globally and locally)
- Local importance used for recommendation interventions?
- Lapse day and Lapse hour are useful for day and hour level models as expected
- Demographics not particularly important (but limited race/ethnicity diversity)
Positive Predictive Value (PPV)

Positive Predictive Value (PPV)

Positive Predictive Value (PPV)

Impact of Decision Thresholds: 1 day
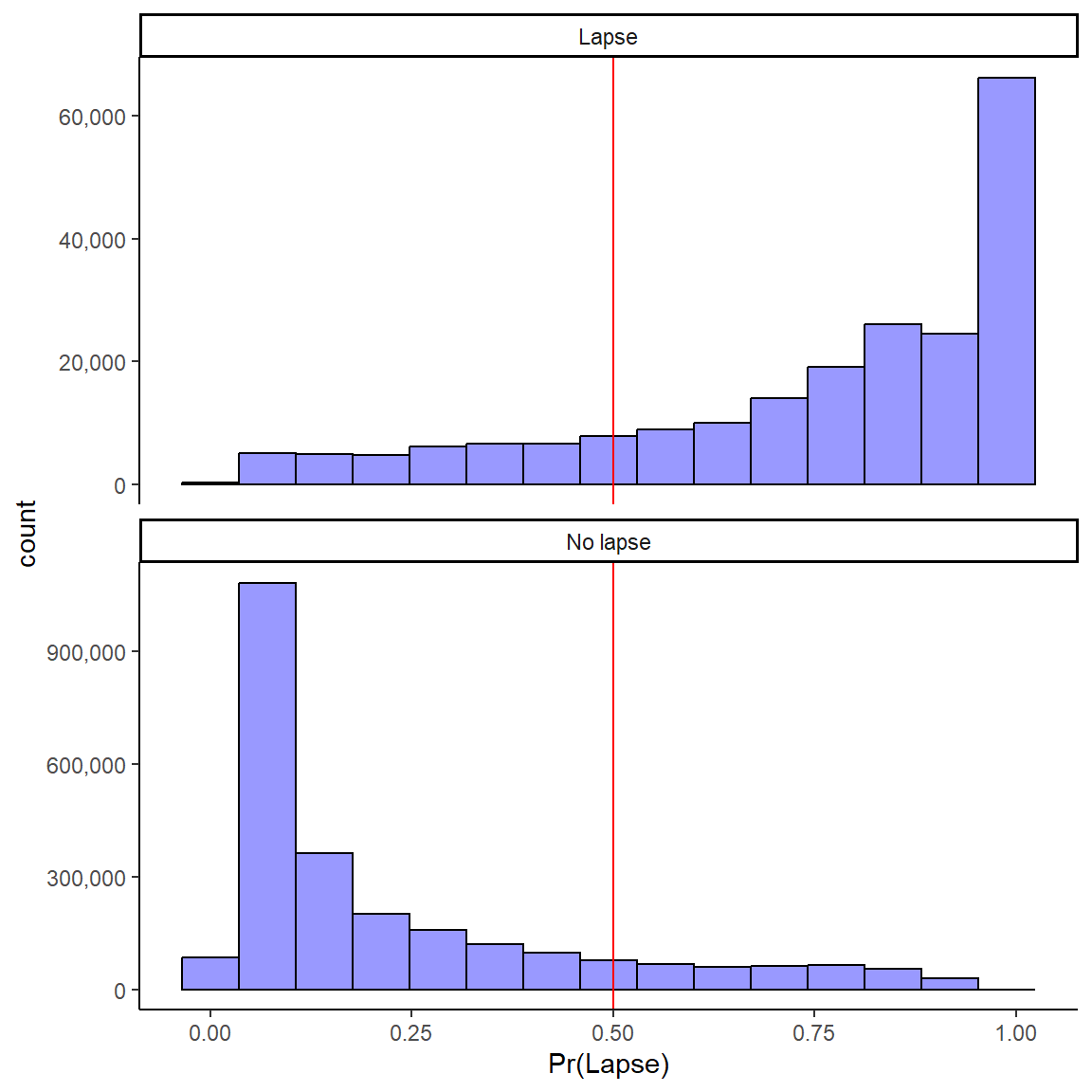

Impact of Decision Thresholds: 1 day

Precision - Recall Curves

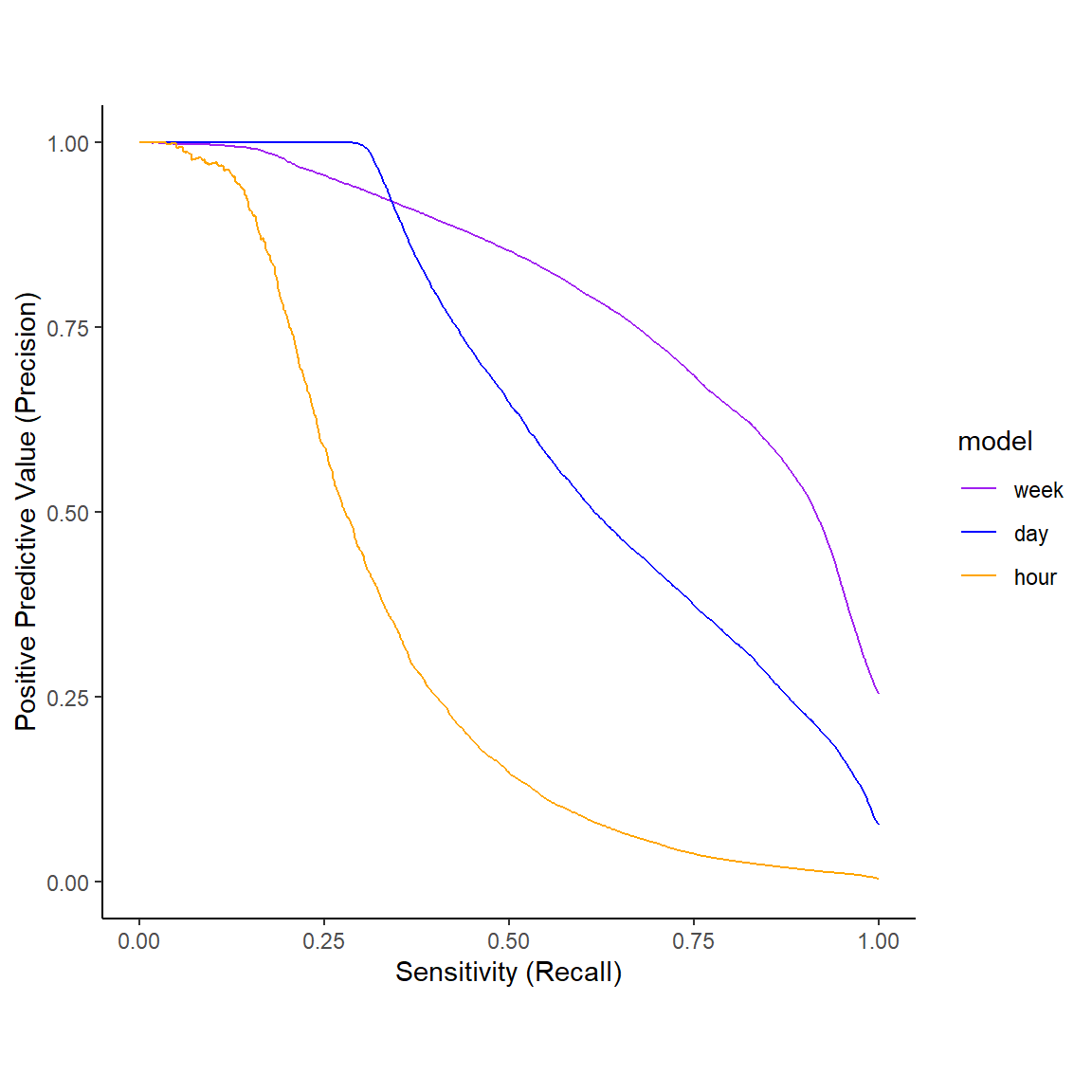
Key Take Home Messages
Relatively high combined sensitivity and specificity
Comparable performance (AUC) from 1 week down to 1 hour windows
Will need to adjust decision thresholds to fit how we use the algorithm.
- Lower PPV OK for low burden or low cost recommendations
- Higher PPV needed to recommend “costly” interventions or actions
(Selective) Next Steps
- Geolocation, cellular communications, and other passively sensed signals
…Imagine my smartphone communications…

Context is Critical
Context is Critical

Context is Critical
Contextualized Geolocation

Contextualized Communications

Baseline Feature Engineering for GPS
Focus on recent past experiences (6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 168 hours)
Raw scores and change scores (from baseline)
Time spent at important places (e.g, alcohol present, drank at location in past, risky, unpleasant)

(Selective) Next Steps
Geolocation, cellular communications, and other passively sensed signals
Build models with lead times > 0 hours
(Selective) Next Steps
Geolocation, cellular communications, and other passively sensed signals
Build models with lead times > 0 hours
More diversity in training data
Active Project: Lapse in patients with Opioid Use Disorder
- Recruiting 400 - 500 patients in recovery from Opioid Use Disorder (~ 300 so far)
- National sample (size; diversity: demographics, location)
- More variation in stage of recover (1 – 6 months at start)
- 12 months of monitoring
- Closer to real implementation methods


(Selective) Next Steps
Geolocation, cellular communications, and other passively sensed signals
Build models with lead times > 0 hours
More diversity in training data
Use models to improve DTx engagement and clinical outcomes
- SMART DTx – algorithm guided use
- How to craft patient feedback to encourage trust in the algorithm
Relapse Prevention Model

Optimization/Evaluation of an Algorithm Guided Smart DTx
- Lapse probabilities updated daily based on EMA and Geolocation features
- Use lapse probability and locally important features to select optimal DTx modules – guided by Rela
- Provide recommendations designed to encourage engagement
- Algorithm transparency (risk level, change, features)
- Communication factors (empathy, feasibility)
- MRT to optimize recommendation message components
- RCT to evaluate Standard vs. Smart DTx on clinical outcomes

CRediTs
 ::: {.notes}
::: {.notes}
:::